DIY Pure Sine Wave Inverter Making At Home
DIY Pure Sine Wave Inverter Making at Home Using EGS002 Module: A Complete Guide
Building your own pure sine wave inverter can be a rewarding and educational DIY project. A pure sine wave inverter produces a smooth, consistent waveform similar to what we receive from the utility grid, making it ideal for sensitive electronics. In this guide, we’ll show you how to build a pure sine wave inverter using the EGS002 module and other essential components, with PCB support from PCBWay for a professional touch. Follow along to create your own high-quality, efficient inverter for your home power backup needs.

Why Choose a Pure Sine Wave Inverter?
A pure sine wave inverter is the best choice for high-performance electronics, as it produces a stable waveform, making it suitable for sensitive devices like computers, medical equipment, and other advanced electronics. This DIY project provides you with a cost-effective, high-efficiency inverter tailored to your requirements.
Essential Components for the DIY Pure Sine Wave Inverter
Here’s a list of components you’ll need for this project:
EGS002 Module: This module serves as the control brain of the inverter, managing the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to achieve a pure sine wave.
IRFZ44N MOSFET (4 pieces): High-efficiency MOSFETs that switch DC to AC power.
FR107 (4 pieces): Fast recovery diodes to improve efficiency.
Capacitors: Various capacitors help filter and stabilize the circuit.
2200uF, 35V x 4P
100uF, 25V x 2P
10uF, 50V
104 ceramic capacitors x 6P
103VR: Voltage regulator for stable output.
L7805 Voltage Regulator: Regulates the voltage for stable control.
Resistors:
100K x 2P
1K x 2P
2.2K
10R x 4P
4.7K x 4P
Switch: Controls the inverter operation.
NTC 10K Thermistor: Detects temperature changes and protects against overheating.
Heatsink: Essential for dissipating heat generated by the MOSFETs.
225J Feedback Capacitor: Maintains waveform quality.
DC 12V Fan: For cooling the inverter.
UPS Transformer: Steps up the voltage from DC to AC.
LED: For power indication.
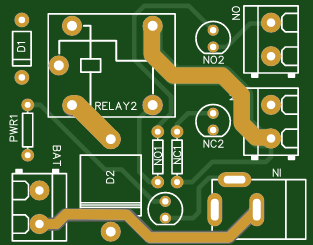
PCB: PCBWay offers quality custom PCBs to enhance circuit stability.
Wires: For making connections between components.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building the Pure Sine Wave Inverter

Step 1: Preparing the EGS002 Module
The EGS002 module provides the necessary control signals for pure sine wave output. Place the module on a PCB designed with high voltage circuits and PWM controls. Solder it carefully, ensuring all connections are secure.
Step 2: Assembling the MOSFETs and Heatsink
The IRFZ44N MOSFETs are responsible for switching power efficiently. Connect four IRFZ44N MOSFETs in parallel to handle high current, and mount them on a heatsink to prevent overheating. This setup will ensure stable power output without excessive heat.
Step 3: Adding the Capacitors and Diodes
Next, connect the capacitors and FR107 diodes. The capacitors (especially the 2200uF, 35V ones) help smooth out any voltage ripples, while the FR107 diodes allow for fast recovery and efficient circuit performance. Be sure to check polarity when soldering capacitors and diodes.
Step 4: Voltage Regulation and Filtering
Install the L7805 voltage regulator to ensure a consistent 5V for sensitive components. Additionally, place 100uF and 10uF capacitors to filter noise and stabilize the voltage. The 225J feedback capacitor maintains the waveform, ensuring a clean pure sine wave output.
Step 5: Installing the Resistors and Thermistor
Add resistors of various values as per the design, focusing on positions that control current flow and protect other components. The NTC 10K thermistor is vital for temperature protection, adjusting resistance according to heat and protecting the system from overheating.
Step 6: Transformer Connection
The transformer converts DC input to AC output. Connect it securely to the MOSFET output stage and the 12V DC input. Ensure that the transformer is rated to handle the power load you need and is wired correctly for safety and efficiency.
Step 7: Connecting the Fan and Final Components
A DC 12V fan will help dissipate heat, especially when the inverter runs continuously. Mount the fan near the MOSFETs and heatsink. Connect the LED to indicate power status, and add a switch to turn the inverter on and off.
Step 8: Final Assembly and Testing
After wiring all components, assemble everything neatly on a PCB from PCBWay, which can enhance the durability and safety of your project. Once assembled, test the inverter with a multimeter, checking for stable output voltage and a smooth waveform.
Key Tips for Success
Ensure Secure Connections: Solder connections securely to avoid loose components.
Use a Quality PCB: PCBWay provides affordable, high-quality custom PCBs, ensuring circuit stability.
Double-Check Polarity: Incorrect polarity in capacitors and diodes can damage your circuit.
Proper Cooling: The MOSFETs generate heat; a heatsink and fan are essential to prevent overheating.
Safety First: Always disconnect power while making adjustments, and take necessary safety precautions.
Why Choose PCBWay for Your DIY Projects?
PCBWay offers reliable, custom-made PCBs that are ideal for DIY electronics projects. Their easy-to-order process and affordable rates make them the perfect choice for hobbyists and professionals. With PCBWay, you get quality, durability, and performance to enhance your projects.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the EGS002 module?
The EGS002 module is a popular inverter control module that uses PWM to produce a pure sine wave output, ideal for powering sensitive electronics.
2. Can I use other MOSFETs?
While IRFZ44N MOSFETs are recommended for their efficiency, other MOSFETs with similar ratings can work, though the circuit may need adjustment.
3. Why is a pure sine wave inverter better?
Pure sine wave inverters provide a consistent, smooth AC waveform that is compatible with most electronics, preventing the risk of damage from waveform irregularities.
4. Is this inverter suitable for high power loads?
This setup is suitable for medium loads but can be scaled up by using higher-rated components and MOSFETs.
Video Reference:
Conclusion
Building a pure sine wave inverter using the EGS002 module and quality components offers an efficient and reliable power source for home use. This DIY guide provides an accessible approach to constructing an inverter with professional-grade performance. Whether you’re interested in learning about electronics or need a cost-effective solution, this project combines technical learning with practical application.
Explore PCBWay to order custom PCBs and bring your DIY projects to life with ease! Happy building!
DIY Pure Sine Wave Inverter Making At Home
*PCBWay community is a sharing platform. We are not responsible for any design issues and parameter issues (board thickness, surface finish, etc.) you choose.
- Comments(0)
- Likes(4)
-
 Sergio Oliveira
May 29,2025
Sergio Oliveira
May 29,2025
-
 Engineer
Dec 22,2024
Engineer
Dec 22,2024
-
 Engineer
Nov 15,2024
Engineer
Nov 15,2024
-
 RichardV31
Nov 01,2024
RichardV31
Nov 01,2024
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by Estiak Khan
More by Estiak Khan
-
 ⚡ How to Make a DIY Spot Welding Machine at Home for 18650 Batteries | Full Circuit & Working
If you’re working on battery pack projects using 18650 lithium-ion cells, then you know how importan...
⚡ How to Make a DIY Spot Welding Machine at Home for 18650 Batteries | Full Circuit & Working
If you’re working on battery pack projects using 18650 lithium-ion cells, then you know how importan...
-
 🔋 How to Make a Simple DIY Wi-Fi Router UPS at Home | Step-by-Step Guide with Circuit & PCB
Do you lose internet connection every time the power goes out?If yes, then this simple DIY Wi-Fi Rou...
🔋 How to Make a Simple DIY Wi-Fi Router UPS at Home | Step-by-Step Guide with Circuit & PCB
Do you lose internet connection every time the power goes out?If yes, then this simple DIY Wi-Fi Rou...
-
 Automatic AC Changeover for Inverter
Automatic AC Changeover for Inverter – DIY Circuit GuideAre you tired of manually switching between ...
Automatic AC Changeover for Inverter
Automatic AC Changeover for Inverter – DIY Circuit GuideAre you tired of manually switching between ...
-
 How to Make a 12V AC/DC Fan Controller Module
If you're looking for an efficient way to control a 12V fan using either AC or DC input, this DIY pr...
How to Make a 12V AC/DC Fan Controller Module
If you're looking for an efficient way to control a 12V fan using either AC or DC input, this DIY pr...
-
 Autocut DC Mini IPS for DC 12V Load
Autocut DC Mini IPS for DC 12V LoadIf you are looking for a reliable Autocut DC Mini IPS for DC 12V ...
Autocut DC Mini IPS for DC 12V Load
Autocut DC Mini IPS for DC 12V LoadIf you are looking for a reliable Autocut DC Mini IPS for DC 12V ...
-
 Build a 12V Battery Autocut System with LCD Display
Are you looking for an efficient and affordable way to protect and monitor your 12V battery system? ...
Build a 12V Battery Autocut System with LCD Display
Are you looking for an efficient and affordable way to protect and monitor your 12V battery system? ...
-
 DIY Transistor Tester | Build Your Own LCR Meter at Home with Arduino Nano
Are you fascinated by electronics and want to create your own tools for testing components? Building...
DIY Transistor Tester | Build Your Own LCR Meter at Home with Arduino Nano
Are you fascinated by electronics and want to create your own tools for testing components? Building...
-
 How to Make a Pure Sine Wave Inverter Using EG8010 + IR2110S | Step-by-Step Guide
How to Make a Pure Sine Wave Inverter Using EG8010 + IR2110S | Step-by-Step GuideIf you are looking ...
How to Make a Pure Sine Wave Inverter Using EG8010 + IR2110S | Step-by-Step Guide
How to Make a Pure Sine Wave Inverter Using EG8010 + IR2110S | Step-by-Step GuideIf you are looking ...
-
 🔋 How to Make DC Changeover for Automatic Inverter System | DIY Inverter Changeover Switch
Are you tired of manually switching between DC power supply and battery backup during load shedding?...
🔋 How to Make DC Changeover for Automatic Inverter System | DIY Inverter Changeover Switch
Are you tired of manually switching between DC power supply and battery backup during load shedding?...
-
 No Need Adapter 🤔 WiFi Router UPS Making with Transformer
No Need Adapter WiFi Router UPS Making with Transformer | Complete Circuit DiagramAre you tired of ...
No Need Adapter 🤔 WiFi Router UPS Making with Transformer
No Need Adapter WiFi Router UPS Making with Transformer | Complete Circuit DiagramAre you tired of ...
-
 🔋 How to Make a Power Bank Module at Home
Are you looking to build your own DIY power bank at home? In this blog post, we’ll show you how to c...
🔋 How to Make a Power Bank Module at Home
Are you looking to build your own DIY power bank at home? In this blog post, we’ll show you how to c...
-
 Cute LIT 220W Inverter Load Test ⚡ Auto Changeover IPS System Explained! 🔋 Real Load Backup Test
Are you looking for a reliable backup power solution for your WiFi router, CCTV, or small appliances...
Cute LIT 220W Inverter Load Test ⚡ Auto Changeover IPS System Explained! 🔋 Real Load Backup Test
Are you looking for a reliable backup power solution for your WiFi router, CCTV, or small appliances...
-
 ⚡ Hybrid WiFi Router UPS for Solar System
IntroductionPower cuts in off-grid areas can disrupt internet connectivity. With the rise of solar s...
⚡ Hybrid WiFi Router UPS for Solar System
IntroductionPower cuts in off-grid areas can disrupt internet connectivity. With the rise of solar s...
-
 🔋 DIY Solar-Based Mini IPS at Home | Auto Load Changeover Circuit for 12V DC Fan/Light
If you're looking for an easy and affordable solution to keep your 12V DC fan or light running even ...
🔋 DIY Solar-Based Mini IPS at Home | Auto Load Changeover Circuit for 12V DC Fan/Light
If you're looking for an easy and affordable solution to keep your 12V DC fan or light running even ...
-
 🔋 DIY Automatic Cut Off 12V Trickle Charger | Lead Acid Battery AutoCut Charger
Do you often charge your 12V lead-acid battery manually and worry about overcharging? With this DIY ...
🔋 DIY Automatic Cut Off 12V Trickle Charger | Lead Acid Battery AutoCut Charger
Do you often charge your 12V lead-acid battery manually and worry about overcharging? With this DIY ...
-
 🔥 DIY Smart 12V Battery at Home | Using 18650 Cells + Smart BMS
Looking for a way to build a powerful and smart 12V battery at home? In this guide, I'll show you h...
🔥 DIY Smart 12V Battery at Home | Using 18650 Cells + Smart BMS
Looking for a way to build a powerful and smart 12V battery at home? In this guide, I'll show you h...
-
 🎮 DIY Arduino Nano Snake Game Console with OLED Display
DIY Arduino Nano Snake Game Console with OLED Display and ButtonsDo you love retro games? Want to bu...
🎮 DIY Arduino Nano Snake Game Console with OLED Display
DIY Arduino Nano Snake Game Console with OLED Display and ButtonsDo you love retro games? Want to bu...
-
 DIY 150W IPS Making At Home with Auto Changeover System | Mini IPS 2025
How to Make an Automatic 150W IPS Using Two Circuit ModulesAre you looking for a reliable and effici...
DIY 150W IPS Making At Home with Auto Changeover System | Mini IPS 2025
How to Make an Automatic 150W IPS Using Two Circuit ModulesAre you looking for a reliable and effici...
-
-
mammoth-3D SLM Voron Toolhead – Manual Drill & Tap Edition
207 0 0 -
-
AEL-2011 Power Supply Module
730 0 2 -
AEL-2011 50W Power Amplifier
607 0 2 -
-
-
Custom Mechanical Keyboard
812 0 0 -
Tester for Touch Screen Digitizer without using microcontroller
438 2 2 -
Audio reactive glow LED wristband/bracelet with NFC / RFID-Tags
391 0 1 -
-