|
KiCADKicad
|
3-Way Monophonic Equalizer
Introduction
This project is a high-fidelity monophonic equalizer featuring a 3-band active filter network built around the LM358N op-amp. Designed for precise tone control, it includes bass, midrange, and treble stages, offering smooth frequency shaping for audio enthusiasts and DIY builders alike.

Figure 1. Equalizer Block Diagram
Features
- Based on a classic op-amp active filter topology
- Uses a single op-amp IC (LM358 or similar)
- Separate tone controls: bass, mid, and treble
- Designed for mono audio signal processing
- Powered by dual supply ±12V (or ±15V)
Circuit Diagram
Basically, circuits from an equalizer are formed by a filters network for different audio frequency bands.

Figure 2. Equalizer Circuit Diagra
The rotary potentiometers P1, P2, and P3 allow the frequency response of bass, midrange, and treble to be adjusted to approximately -20 dB of cut, flat response, and +20 dB of boost.
Frequency Response
Almost any overall gain-vs-frequency characteristic can be defined by the design of feedback network. The composite frequency response curves shown in Figure 3 are provided by the component values indicated in the circuit diagram (Figure 2).

Figure 3. Equalizer Frequency Response Curves
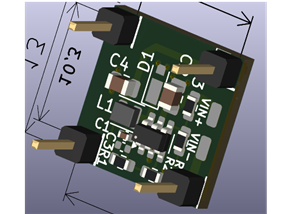
PCB Design
This board is ideal for DIY audio preamps, sound experiments, or as part of a larger analog synthesizer or effects unit.

Figure 4. PCB Dimensions and Details
🛠 PCB size and component layout are optimized for easy prototyping and panel mounting.
📌 Gerber download is disabled. To get the board, please use the add to cart option.
Source
Full circuit diagram, theoretical explanation, component values, and test results are available in the original article (in Spanish):
https://blogtronika.blogspot.com/2018/01/ecualizador-monofonico-tres-tonos.html
3-Way Monophonic Equalizer
*PCBWay community is a sharing platform. We are not responsible for any design issues and parameter issues (board thickness, surface finish, etc.) you choose.
- Comments(0)
- Likes(0)
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by Audio Leo
More by Audio Leo
-
-
AEL-2011 Power Supply Module
553 0 2 -
AEL-2011 50W Power Amplifier
512 0 2 -
-
-
Custom Mechanical Keyboard
710 0 0 -
Tester for Touch Screen Digitizer without using microcontroller
340 2 2 -
Audio reactive glow LED wristband/bracelet with NFC / RFID-Tags
322 0 1 -
-
-