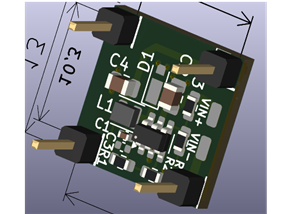
Atari XE 1MB XE SuperCart
XE 1M Cart Instructions (Rev A)
by Bryan Edewaard
This board is designed to fit into the new Mq/Sikor shell and provide up to 1MB of ROM space via bank-switching. It can also be configured for a non bank-switched 16K ROM.
The switching scheme is based on the XE cartridges produced by Atari. Any access within 8000-9FFF will read from the selected 8K bank, and any access within A000-BFFF will read from a fixed bank (the topmost 8K in the ROM). A write to the D5 page (D500-D5FF) sets the current bank.
Theory of operation:
U2 is a 374 8-bit register that holds the selected bank. While accessing A000-BFFF this chip is disabled, and the installed resistors (R1,R2,R3 or RN1) pull all the bank-switching address lines high causing the last bank to be read. While accessing 8000-9FFF the 374 is enabled and the selected bank is read.
U3 is the 28-pin footprint for a 27128-27512. U4 is the 32-pin footprint for a 27010-27080. U1 is a 00 quad NAND gate (combinational logic), and C1 & C2 are .1uF decoupling caps (for noise suppression).
R1, R2, and R3 are the pull-ups for A13, A14, and A15 respectively. In their place RN1 (SIP resistor network) can be used to pull up lines A13-A19
I typically use 74HCT logic with this board, but just about any TTL logic (such as LS, ALS, F, etc.) should work.
Here are the specifics for using different size EPROMs:
-16K (27128):
Resistors: Omit R1, R2 & R3 = jumpers
The bankswitching is disabled for this size and U2 is omitted (install U1, however). In the space for U2, install a jumper between pins 1 & 2. Also install R2 & R3.
-32K (27256):
Resistors: R1 & R2 = 4.7K, R3 = 1K, omit RN1
Set bits 0 and 1 to the desired bank.
With this size EPROM we need to address the problem of the VPP pin (pin 1). This pin is used for A15 in larger EPROMs, so the cartridge is designed to be able to toggle it. But most 27256 EPROMs will stop functioning if this line goes low. Since the 374 is in an unknown state at power-up, we need a way to make sure the EPROM will always respond. There are a couple possible solutions to this problem:
1. The easy method: Bend up (or cut off) pin 6 of the 374 so R3 always keeps VPP pulled high. This method will work regardless of the ROM image (when using this method you can replace R3 with a jumper wire if you wish).
2. The software solution: Set the diagnostic flag in the cartridge. This way, the OS will only check one byte at the end of the cartridge before jumping in so the 374 is never engaged before you get a chance to set it. From then on, always keep bank-select bit 2 set to keep VPP high. Remember that a diagnostic cartridge must initialize the system itself, so you cannot use this option unless you specifically write for it. R3 is 1K to make sure it meets the current requirements for the VPP pin.
-64K (27512)
Resistors: R1, R2 & R3 = 4.7K, omit RN1
No surprises here. Just set bits 0,1 and 2 to the desired bank.
-128K (27010)
Resistors: Omit R1,R2,R3 and install an 8-pin bussed 4.7K network in RN1.
Set bits 0,1,2 and 3 to the desired bank.
-256K-1MB (27020-27080)
Same as above, but add one more bank-select bit for each increase in EPROM size (bit 7 is never used).
Notes:
Always remember that the IC's face the back of an Atari 8-bit computer cartridge.
C1 & C2 can be any small, inexpensive .1uF (usually marked '104') ceramic or monolithic cap.
The board is designed for 1/4 watt resistors. However, 1/8 watt will work too.
Atari XE 1MB XE SuperCart
*PCBWay community is a sharing platform. We are not responsible for any design issues and parameter issues (board thickness, surface finish, etc.) you choose.
- Comments(12)
- Likes(8)
-
 Wojciech Gwioździk
May 06,2025
Wojciech Gwioździk
May 06,2025
-
 James Alexander
Jan 31,2025
James Alexander
Jan 31,2025
-
 Juan VM
Nov 23,2024
Juan VM
Nov 23,2024
-
 Krzysztof Suszczewicz
Mar 22,2024
Krzysztof Suszczewicz
Mar 22,2024
-
 Cristian Rojas
Oct 29,2022
Cristian Rojas
Oct 29,2022
-
 Валентин Матвиенко
Oct 28,2022
Валентин Матвиенко
Oct 28,2022
-
 Francisco Meza
Nov 26,2021
Francisco Meza
Nov 26,2021
-
 (DIY) C64iSTANBUL
Jul 19,2021
(DIY) C64iSTANBUL
Jul 19,2021
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by Christopher Belcher
More by Christopher Belcher
-
 Cheap NESpad to Atari 7800
This is a pcb that should fit in many NES gamepad cases - both original and reproduction and let you...
Cheap NESpad to Atari 7800
This is a pcb that should fit in many NES gamepad cases - both original and reproduction and let you...
-
 DB-9 Atari Commodore Joystick Cable Tester
Got a broken retro joystick? Got replacement joystick cables but you don't know what color wires go...
DB-9 Atari Commodore Joystick Cable Tester
Got a broken retro joystick? Got replacement joystick cables but you don't know what color wires go...
-
 15kHz Monitor Tester Carrier Board for Atari ST and Amiga
Atari ST and Amiga computers used a frequency that many modern VGA monitors cannot deal with - 15kHz...
15kHz Monitor Tester Carrier Board for Atari ST and Amiga
Atari ST and Amiga computers used a frequency that many modern VGA monitors cannot deal with - 15kHz...
-
 Atari 5200 - PC Joystick or Wico 5200 Adapter
This is a dual purpose adapter for 5200 owners. It will let you use a PC joystick with your 5200 and...
Atari 5200 - PC Joystick or Wico 5200 Adapter
This is a dual purpose adapter for 5200 owners. It will let you use a PC joystick with your 5200 and...
-
 32K Super Memory Expander for the VTech Precomputer 2000 / Genius Leader 2000
This is a clone of the 32K Super Memory Expander for the VTech Precomputer 2000 / Genius Leader 2000...
32K Super Memory Expander for the VTech Precomputer 2000 / Genius Leader 2000
This is a clone of the 32K Super Memory Expander for the VTech Precomputer 2000 / Genius Leader 2000...
-
 40 pin wide DIP to ZIF
I sometimes remove chips from retro computers and want to put in ZIF sockets for testing, but the pi...
40 pin wide DIP to ZIF
I sometimes remove chips from retro computers and want to put in ZIF sockets for testing, but the pi...
-
 28 pin wide DIP to ZIF
I sometimes remove chips from retro computers and want to put in ZIF sockets for testing, but the pi...
28 pin wide DIP to ZIF
I sometimes remove chips from retro computers and want to put in ZIF sockets for testing, but the pi...
-
 Atari 65/130XE Production Test Jig - SIO Loop
This is the SIO port loopback cartridge to be used with the Atari 65/130XE Production Test cartridge...
Atari 65/130XE Production Test Jig - SIO Loop
This is the SIO port loopback cartridge to be used with the Atari 65/130XE Production Test cartridge...
-
 Atari 65/130XE Production Test Jig - Joystick Loop
This is the joystick port loopback cartridge to be used with the Atari 65/130XE Production Test cart...
Atari 65/130XE Production Test Jig - Joystick Loop
This is the joystick port loopback cartridge to be used with the Atari 65/130XE Production Test cart...
-
 Genesis Controller to Atari 7800
Will allow you to plug a wired Genesis controller into an Atari 7800 and have 2 button functionality
Genesis Controller to Atari 7800
Will allow you to plug a wired Genesis controller into an Atari 7800 and have 2 button functionality
-
 Atari 5200 Controller Test Fixture
Atari 5200 consoles with controller problems sometimes need their POKEY adjusted to center the contr...
Atari 5200 Controller Test Fixture
Atari 5200 consoles with controller problems sometimes need their POKEY adjusted to center the contr...
-
 DR Rotary Switch Panel
Lets you mount an Alco DR series 16 position rotary switch on a panel - useful for multiROM and mult...
DR Rotary Switch Panel
Lets you mount an Alco DR series 16 position rotary switch on a panel - useful for multiROM and mult...
-
 Atari XE 1MB XE SuperCart
XE 1M Cart Instructions (Rev A)by Bryan EdewaardThis board is designed to fit into the new Mq/Sikor ...
Atari XE 1MB XE SuperCart
XE 1M Cart Instructions (Rev A)by Bryan EdewaardThis board is designed to fit into the new Mq/Sikor ...
-
 Atari Basic ROM multi-adapter
Replaces the 2364 BASIC ROM in Atari XL computers with a 27C1000 to allow you a selection of 16 diff...
Atari Basic ROM multi-adapter
Replaces the 2364 BASIC ROM in Atari XL computers with a 27C1000 to allow you a selection of 16 diff...
-
 Syndrum MIDI to Atari Carrier
A board that uses and Arduino Nano to go from 5pin DIN MIDI to the Atari 2600 Joystick port.To be us...
Syndrum MIDI to Atari Carrier
A board that uses and Arduino Nano to go from 5pin DIN MIDI to the Atari 2600 Joystick port.To be us...
-
 Cheep Talk for Atari 8 Bit Computers
This is a board for the SPO256 chip used in several Atari speech projects in the 1980'sFor an Atari ...
Cheep Talk for Atari 8 Bit Computers
This is a board for the SPO256 chip used in several Atari speech projects in the 1980'sFor an Atari ...
-
 Atari Power Testing Board
Meant to have the connector jacks from the various Atari 8 bit systems - 2600, 800, XL/XE, and 7800 ...
Atari Power Testing Board
Meant to have the connector jacks from the various Atari 8 bit systems - 2600, 800, XL/XE, and 7800 ...
-
-
mammoth-3D SLM Voron Toolhead – Manual Drill & Tap Edition
189 0 0 -
-
AEL-2011 Power Supply Module
715 0 2 -
AEL-2011 50W Power Amplifier
599 0 2 -
-
-
Custom Mechanical Keyboard
798 0 0 -
Tester for Touch Screen Digitizer without using microcontroller
422 2 2 -
Audio reactive glow LED wristband/bracelet with NFC / RFID-Tags
384 0 1 -
-