Semi-automatic welding control board
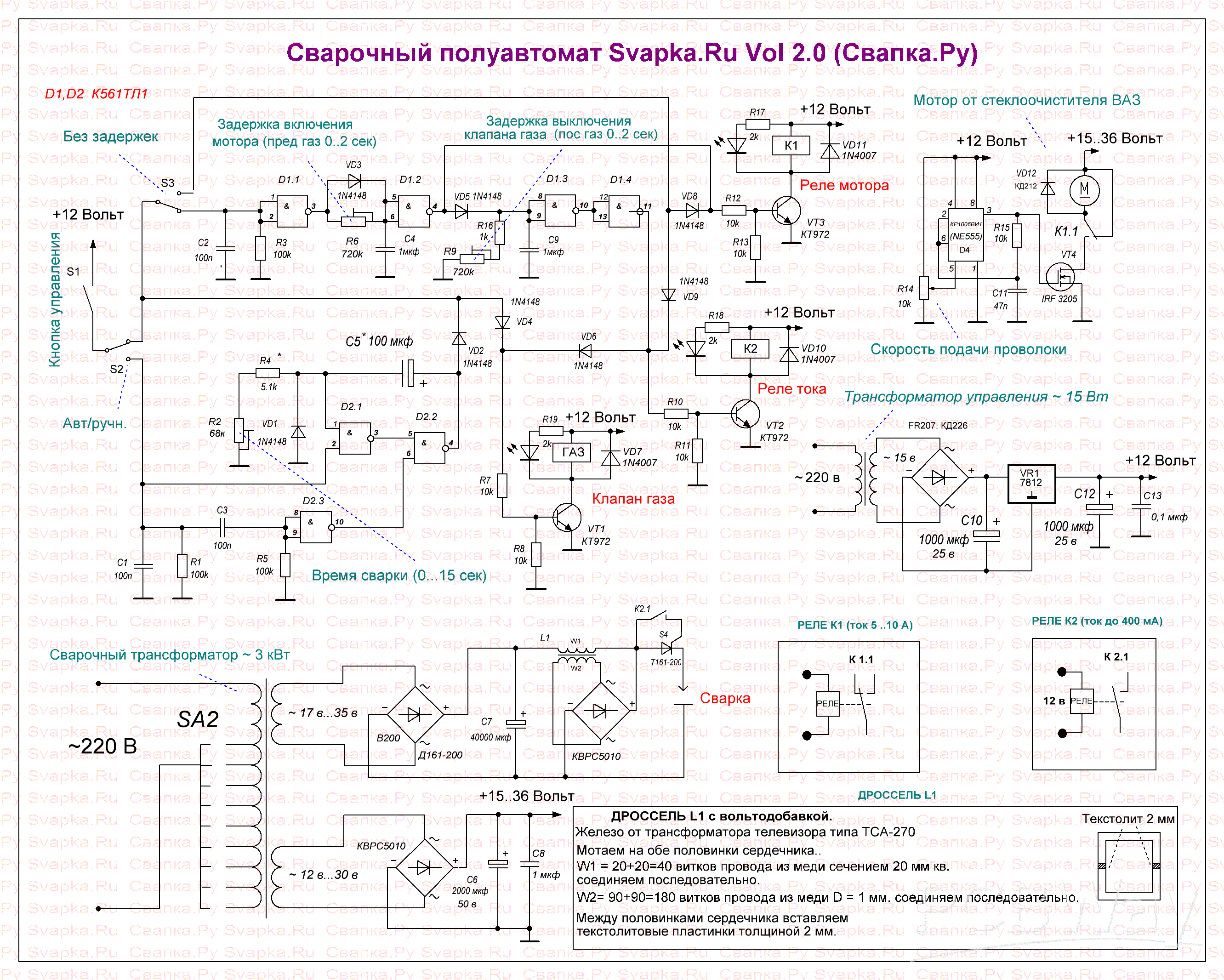
A distinctive feature of this circuit is the use of one voltage source of 12 volts and CMOS series microcircuits, namely CD4096, are used as logic elements in the control unit.
This scheme uses 2 welding modes: manual and automatic.
The circuit has the ability to disable pre-gas and post-gas delays if you don’t need them; we’ll call this operating mode without delays. Also, delays can be turned off if we are welding with cored wire (pre-gas and post-gas delays are of no use here).
_
The operating algorithm is as follows:
1. When you press the control button, carbon dioxide is supplied first, this is done so that the burner is filled with gas.
2. After a delay of 1..3 seconds, the welding current and wire feed are automatically turned on.
3. After releasing the control button, the wire feed is switched off.
4. Then after 1..3 seconds the supply of carbon dioxide is turned off, this is necessary so that the melted metal does not oxidize when cooling, and the welding current is turned off.
_
Manual mode.
The circuit is in its original state, control button SB1 is released. Switch SA1 (Auto/manual) is in the upper position according to the diagram. Switch SA2 (No delays) is in the lower position according to the diagram, that is, the pre-throttle and post-throttle delays are turned on.
When the control button is pressed, logical 1 opens the gas valve through diode VD4. Also starts the delay circuit assembled on D1.1 and D1.2. After the time specified by the chain R6, C4, a logical 1 appears at output 4 of element D1.2, which triggers the motor relay through the diode VD9. At the same time, log 1 appears at output 11 D1.4, which turns on the current relay through the VD6 diode.
At this time, the welding process is underway.
When the control button is pressed, a logical 0 appears at output 4 of element D1.2, which turns off the motor relay. Then, after a time specified by the chain R9, C9, log 0 appears at output 11 of D1.4, which turns off the current relay and gas valve.
At this time the welding is completed.
Auto mode.
The circuit is in its original state, control button SB1 is released. Switch SA1 (Auto/manual) is in the lower position according to the diagram. Switch SA2 (No delays) is in the lower position according to the diagram, that is, the pre-throttle and post-throttle delays are turned on.
The circuit in this mode works according to the same algorithm as in manual mode, only the welding time is set by the chain C2, R5. With these ratings, the welding time is adjustable within 0..15 sec.
I would like to note that the button must be held in this mode. At the end of the time, the circuit itself will stop the welding process.
If you change your mind about welding in automatic mode, just release the control button and welding will stop.
Under No delay mode.
The circuit is in its original state, control button SB1 is released. Switch SA1 (Auto/manual) is in the upper position according to the diagram. Switch SA2 (No delays) is in the upper position according to the diagram, that is, the pre-throttle and post-throttle delays are turned off.
When the control button is pressed, logical 1 through diodes VD4, VD10, VD11 opens the gas valve of the motor relay and the current relay simultaneously, that is, there are no delays. When you release the control button, everything also turns off at the same time.
Same thing in automatic mode.
The mode without delays is needed for the case when we weld with cored wire, when these delays are not needed. Or for some other reason, for example, if there is little gas left (to save money) or you need to quickly grab something, where the quality of the seam is not so important.
Setup.
The device assembled according to this scheme should work immediately without any problems.
The adjustment of the pre-gas and post-gas delay times is regulated by resistors R6 and R9. With these ratings R6, C4 and R9, C9, the maximum delay time is approximately 1 second. If you need more, you can install capacitors C4 and C9 of larger capacity, for example 3 μF.
These capacitors are not polarized. But no one forbids using electrolytic ones instead without changing the circuit.
In automatic mode, you need to select resistor R4 so that there is no empty movement (useless) of resistor R2.
Semi-automatic welding control board
*PCBWay community is a sharing platform. We are not responsible for any design issues and parameter issues (board thickness, surface finish, etc.) you choose.
- Comments(0)
- Likes(3)
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by Epishko Dmitry
More by Epishko Dmitry
-
 Controller for a soldering station
Digital soldering station for solderingrs with cartridges JBC C210 and C245Built on STM32 controller...
Controller for a soldering station
Digital soldering station for solderingrs with cartridges JBC C210 and C245Built on STM32 controller...
-
 IR2153 Power Supply for Power Amplifier
IR2153 Power Supply for Power Amplifier
IR2153 Power Supply for Power Amplifier
IR2153 Power Supply for Power Amplifier
-
 Amplifier JLH1969
Amplifier JLH1969Ultra-linear class A amplifier JLH1969.
Amplifier JLH1969
Amplifier JLH1969Ultra-linear class A amplifier JLH1969.
-
 Power supply for amplifier
Power supply for amplifier!Two power lines: high-current and low-current!
Power supply for amplifier
Power supply for amplifier!Two power lines: high-current and low-current!
-
 Inverter 12-220
Inverter 12-220Power 300WModified sine wave
Inverter 12-220
Inverter 12-220Power 300WModified sine wave
-
 PWM controller tester SG3525
Checking work:error amplifierfrequencydead timesoft startshutdown
PWM controller tester SG3525
Checking work:error amplifierfrequencydead timesoft startshutdown
-
 Protection system for powerful power amplifier
The printed circuit board is made according to the diagram shown. With the exception of power supply...
Protection system for powerful power amplifier
The printed circuit board is made according to the diagram shown. With the exception of power supply...
-
 Hi-Fi inverting amplifier on TDA7293 / 7294 with T-shaped feedback
Why is it needed - inverting switching? There are two reasons: firstly, to get rid of the electrolyt...
Hi-Fi inverting amplifier on TDA7293 / 7294 with T-shaped feedback
Why is it needed - inverting switching? There are two reasons: firstly, to get rid of the electrolyt...
-
 Semi-automatic welding control board
A distinctive feature of this circuit is the use of one voltage source of 12 volts and CMOS series m...
Semi-automatic welding control board
A distinctive feature of this circuit is the use of one voltage source of 12 volts and CMOS series m...
-
 Transformer winding commutator, fan speed thermostat.
Transformer winding commutator, fan speed thermostat. Requires a separate power source, since contro...
Transformer winding commutator, fan speed thermostat.
Transformer winding commutator, fan speed thermostat. Requires a separate power source, since contro...
-
 Amplifier JLH1969
Ultra-linear class A amplifier JLH1969.
Amplifier JLH1969
Ultra-linear class A amplifier JLH1969.
-
 Electronic load
Operating principle: current stabilizer!The power depends on the transistors you use!Possibility of ...
Electronic load
Operating principle: current stabilizer!The power depends on the transistors you use!Possibility of ...
-
 Controller for soldering irons with cartridges JBC C210 and C245 and RT-series from WELLER
Digital soldering stationFor soldering irons with cartridgesJBC C210 and C245and RT-series from WELL...
Controller for soldering irons with cartridges JBC C210 and C245 and RT-series from WELLER
Digital soldering stationFor soldering irons with cartridgesJBC C210 and C245and RT-series from WELL...
-
 JLH Class A Headphone Amplifier
High-quality two-channel headphone amplifier with power supply.The amplifier is powered from a trans...
JLH Class A Headphone Amplifier
High-quality two-channel headphone amplifier with power supply.The amplifier is powered from a trans...
-
 Thyristor charger for car batteries Resurs-1
Charger Resurs-1Manual operation:- current adjustment.Auto mode:- current adjustment.- short circuit...
Thyristor charger for car batteries Resurs-1
Charger Resurs-1Manual operation:- current adjustment.Auto mode:- current adjustment.- short circuit...
-
 Linear laboratory power supply
It is very important to observe the voltage drop on a power transistor, so switching windings is ver...
Linear laboratory power supply
It is very important to observe the voltage drop on a power transistor, so switching windings is ver...
-
-
mammoth-3D SLM Voron Toolhead – Manual Drill & Tap Edition
136 0 0 -
-
AEL-2011 Power Supply Module
643 0 2 -
AEL-2011 50W Power Amplifier
560 0 2 -
-
-
Custom Mechanical Keyboard
762 0 0 -
Tester for Touch Screen Digitizer without using microcontroller
392 2 2 -
Audio reactive glow LED wristband/bracelet with NFC / RFID-Tags
361 0 1 -
-