|
servomotor |
x 4 | |

|
BLUETOOTH-SERIAL-HC-06Olimex Ltd.
|
x 1 | |

|
Arduino Nano V3 |
x 1 | |

|
16 pin female header |
x 1 | |

|
2Pin Screw Terminals 5mm Pitch |
x 1 |

|
arduino IDEArduino
|
|

|
MIT App InventorMIT
|
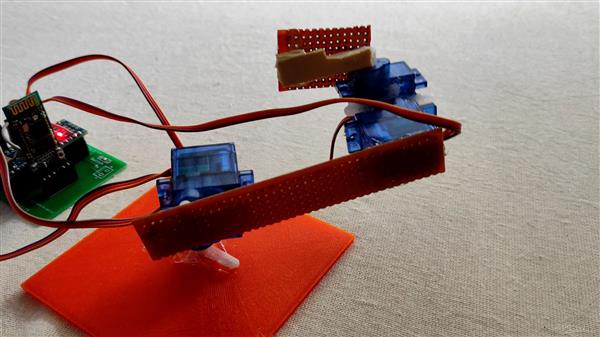
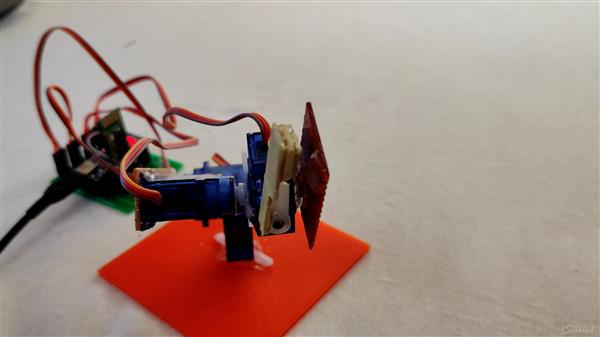
Bluetooth Servo Controller
In this project I am going to show you how you can control a servo motor with the help of a smartphone application via Bluetooth.
For this project we will be using a Bluetooth HC-05 module with an Arduino Uno to control a servo 9g.
How does this project works?
This project has two parts:
1. The android application - This application will be sending various data packets to our HC-05 Bluetooth module
2. The hardware - This consists of HC-05 Bluetooth module, an Arduino Uno and a servo motor.

--> This is how it works --
The android app sends data packets to the Bluetooth module. The Bluetooth modules sends this data packet to Arduino Uno through Serial Communication. Arduino Uno is programmed to generate control signal for the servo motor depending upon the value of the data packet. Here is a flowchart for better understanding.

Flowchart
--> How to get Started
1. Download the android application.
2. Upload the code on the Arduino uno.
3. Make the connections.

Please note that the bluetooth HC-05 module needs to be connected with 3.3v and not with 5v vcc as it can damage the module.
4. Connect Bluetooth module to android app - When you power up your Hardware the Bluetooth module will become visible. So open the application and click on find nearby devices. Select HC-05. Once it shows connected you are good to go!
You can use the slider or enter the value manually to control the servo arm.
Servo motors are largely used in robotics for precise control. Anyone – well, almost anyone – has mobile devices with Bluetooth connection capabilities. In this tutorial, you will find how to wirelessly control a servo motor with an Arduino UNO and an Android device via a Bluetooth connection. In the end, you will be more connected, you will make things easier and control servo motors at the touch of a touchscreen.
In this article, I will introduce you to Bluetooth connections with the HC-06 Bluetooth module, Arduino UNO, and the SG90 servo motor. Also, you need extra resources for this tutorial such as an Android smartphone with Bluetooth capabilities and an application to send commands from smartphone to the Bluetooth module.
In the first part of the tutorial, I will show you how to hook up the HC-06 Bluetooth module to the Arduino. In the second part, you can find the source code to enter in AT command mode of the HC-06 Bluetooth module. Here you’ll set the name of your device, password, and the baud rate of the HC-06 module. Finally, in the last part, you will see how to setup the Android application and how to program Arduino to turn the servo motor at the touch of a button.
Requirements
Connect the right pieces and make them communicate with each other. This is the plan of this project. If you already have all the below parts or a part of them, you are lucky. The whole project will cost you nothing, or a few dollars in case you will buy only the missing parts. Otherwise, you have to spend tens of dollars to buy the servo motor, the Bluetooth module, the development board and few other accessories. To have a clear view of the costs, in the right side of each part and accessory used in this project is a link to an online store. Here are the parts:
1 X Arduino UNO (Amazon) – the Bluetooth module is compatible with almost any Arduino model, but all the code and schematics in this tutorial are for UNO.
1 X HC-06 (Amazon) – this is a slave Bluetooth module very easy to use with Arduino using serial communication.
1 X SG90 Servo Motor (Amazon) – this is probably the most popular servo motor in the DIY community.
7 X male to male jumper wires (Amazon).
1 X breadboard (Amazon).
1 X Android smartphone (Amazon).
Setting Up the Hardware
In this section, I will show you how to wire the Arduino UNO and the HC-06 Bluetooth module.
To use the HC-06 module, simply connect the VCC pin to the 3.3V output on the Arduino, the GND pin to any of Arduino GND pins, then connect the TX pin of the Bluetooth module to pin 10 of Arduino UNO and RX pin of Bluetooth to pin 11 of Arduino.
For servo motor, connect the brown wire to any of Arduino GND pins, the red wire from the SG90 servo to the 5V output of the Arduino, and the orange wire from the servo motor to digital pin 9 of Arduino.
Arduino Sketch and AT Commands
If the Bluetooth module is being used for the first time, you have to interrogate it to change some of the settings. The settings are changed with so-called AT commands.
The HC-06 module allows you to change a limited number of settings. You can change the name of the device, the PIN, and the baud rate.
You have to run the below AT commands in the IDE used with Arduino. These commands show you the version of firmware installed on the HC Bluetooth module, change the PIN, change the name of the module, and set the baud rate at 9600.
#define BLUETOOTH_SPEED 9600 //This is the default baud rate that HC-06 uses
SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 11); // TX | RX
// Connect the HC-06 TX to Arduino pin 10 RX.
// Connect the HC-06 RX to Arduino pin 11 TX.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Starting the configurations!");
mySerial.begin(BLUETOOTH_SPEED);
delay(1000);
// Should respond with OK
Serial.print("AT test command is: ");
mySerial.print("AT");
waitResponse();
Serial.println("----------------");
// Should respond with its version
Serial.print("AT version is: ");
mySerial.print("AT+VERSION");
waitResponse();
Serial.println("----------------");
// Set pin
Serial.print("Set pin: ");
mySerial.print("AT+PIN1234");
waitResponse();
Serial.println("----------------");
// Set the name to ROBOT_NAME
Serial.print("Set the name: ");
String rnc = String("AT+NAME") + String(ROBOT_NAME);
mySerial.print(rnc);
waitResponse();
//Set baudrate to 9600
//AT+BAUD1 OK1200 Sets the baud rate to 1200
//AT+BAUD2 OK2400 Sets the baud rate to 2400
//AT+BAUD3 OK4800 Sets the baud rate to 4800
//AT+BAUD4 OK9600 Sets the baud rate to 9600
//AT+BAUD5 OK19200 Sets the baud rate to 19200
//AT+BAUD6 OK38400 Sets the baud rate to 38400
//AT+BAUD7 OK57600 Sets the baud rate to 57600
//AT+BAUD8 OK115200 Sets the baud rate to 115200
//AT+BAUD9 OK230400 Sets the baud rate to 230400
//AT+BAUDA OK460800 Sets the baud rate to 460800
//AT+BAUDB OK921600 Sets the baud rate to 921600
//AT+BAUDC OK1382400 Sets the baud rate to 1382400
Serial.println("----------------");
// Set baud rate to 9600
Serial.print("Set baud rate: ");
mySerial.print("AT+BAUD4");
waitResponse();
Serial.println("The configurations are done!");
}
void loop() {
}
void waitResponse() {
delay(2000);
while (mySerial.available()) {
Serial.write(mySerial.read());
}
Serial.write("\n");
}
The Android Application and the Arduino Sketch
We’re very close to wirelessly control the SG90 servo motor with an Android smartphone. This is usually done by using an Android application that enables the Bluetooth features of the device.
From many applications that enable the Bluetooth features on Android devices, I choose the Arduino Bluetooth Controller application because is free and easy to use.
Before running the Android application, you make sure that the HC-06 Bluetooth module is up and running.
After the application is installed on your device, you have to scan for devices, enter the PIN number set with the script above, and connect the Bluetooth module.
For this tutorial, I use the “Controller Mode” for commands.
 For this tutorial, I use “Controller Mode”
For this tutorial, I use “Controller Mode”
The interface layout provides 10 buttons specifically designed to send continuously commands while pressed. For now, we only use two of the buttons: one button to send “1”, and another to send “2”. So, use the settings of the application to set the value “1” and value “2” for two of the buttons. These values will be received by the Bluetooth module and used in the Arduino sketch to control the servo motor.

I use these two buttons to send the commands to the Bluetooth module
After the Android application setup is finished, we have to turn back to the Arduino and upload the code to control the servo motor. Below is the Arduino sketch to turn the servo motor at a specific position.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <Servo.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 11); // RX | TX
Servo servo;
int servoPin = 9;
int servoAngle = 0; // servo position in degrees
char command;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
mySerial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("You're connected via Bluetooth");
servo.attach(servoPin);
}
void loop() {
if (mySerial.available())
{
command=(mySerial.read());
if (command=='1')
{
Serial.println("Servo motor to 10 degrees");
servo.write(10);
delay(500);
}
else if (command=='2')
{
Serial.println("Servo motor to 120 degrees");
servo.write(120);
delay(500);
}
}
}
Bluetooth Servo Controller
*PCBWay community is a sharing platform. We are not responsible for any design issues and parameter issues (board thickness, surface finish, etc.) you choose.
- Comments(0)
- Likes(0)
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by Sreeram.zeno
More by Sreeram.zeno
-
 Esp12-F Cluster V1.0
The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip, with built-in TCP/IP networking software, and microcontro...
Esp12-F Cluster V1.0
The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip, with built-in TCP/IP networking software, and microcontro...
-
 TB6612FNG Motor Driver
The TB6612FNG Motor Driver can control up to two DC motors at a constant current of 1.2A (3.2A peak)...
TB6612FNG Motor Driver
The TB6612FNG Motor Driver can control up to two DC motors at a constant current of 1.2A (3.2A peak)...
-
 Sunny Buddy Solar Charger v1.0
This is the Sunny Buddy, a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) solar charger for single-cell LiPo ba...
Sunny Buddy Solar Charger v1.0
This is the Sunny Buddy, a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) solar charger for single-cell LiPo ba...
-
 Diy 74HC4051 8 Channel Mux Breakout Pcb
The 74HC4051; 74HCT4051 is a single-pole octal-throw analog switch (SP8T) suitable for use in analog...
Diy 74HC4051 8 Channel Mux Breakout Pcb
The 74HC4051; 74HCT4051 is a single-pole octal-throw analog switch (SP8T) suitable for use in analog...
-
 Diy RFM97CW Breakout Pcb
IntroductionLoRa? (standing for Long Range) is a LPWAN technology, characterized by a long range ass...
Diy RFM97CW Breakout Pcb
IntroductionLoRa? (standing for Long Range) is a LPWAN technology, characterized by a long range ass...
-
 ProMicro-RP2040 Pcb
The RP2040 is a 32-bit dual ARM Cortex-M0+ microcontroller integrated circuit by Raspberry Pi Founda...
ProMicro-RP2040 Pcb
The RP2040 is a 32-bit dual ARM Cortex-M0+ microcontroller integrated circuit by Raspberry Pi Founda...
-
 Serial Basic CH340G Pcb
A USB adapter is a type of protocol converter that is used for converting USB data signals to and fr...
Serial Basic CH340G Pcb
A USB adapter is a type of protocol converter that is used for converting USB data signals to and fr...
-
 Mp3 Shield For Arduino
Hardware OverviewThe centerpiece of the MP3 Player Shield is a VS1053B Audio Codec IC. The VS1053B i...
Mp3 Shield For Arduino
Hardware OverviewThe centerpiece of the MP3 Player Shield is a VS1053B Audio Codec IC. The VS1053B i...
-
 MRK CAN Shield Arduino
The CAN-BUS Shield provides your Arduino or Redboard with CAN-BUS capabilities and allows you to hac...
MRK CAN Shield Arduino
The CAN-BUS Shield provides your Arduino or Redboard with CAN-BUS capabilities and allows you to hac...
-
 AVR ISP Programmer
AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology ...
AVR ISP Programmer
AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology ...
-
 Diy Arduino mega Pcb
The Arduino Mega 2560 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560. It has 54 digital input/ou...
Diy Arduino mega Pcb
The Arduino Mega 2560 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560. It has 54 digital input/ou...
-
 Max3232 Breakout Board
MAX3232 IC is extensively used for serial communication in between Microcontroller and a computer fo...
Max3232 Breakout Board
MAX3232 IC is extensively used for serial communication in between Microcontroller and a computer fo...
-
 Line Follower Pcb
The Line Follower Array is a long board consisting of eight IR sensors that have been configured to ...
Line Follower Pcb
The Line Follower Array is a long board consisting of eight IR sensors that have been configured to ...
-
 HMC6343 Accelerometer Module
The HMC6343 is a solid-state compass module with tilt compensation from Honeywell. The HMC6343 has t...
HMC6343 Accelerometer Module
The HMC6343 is a solid-state compass module with tilt compensation from Honeywell. The HMC6343 has t...
-
 RTK2 GPS Module For Arduino
USBThe USB C connector makes it easy to connect the ZED-F9P to u-center for configuration and quick ...
RTK2 GPS Module For Arduino
USBThe USB C connector makes it easy to connect the ZED-F9P to u-center for configuration and quick ...
-
 Arduino Explora Pcb
The Arduino Esplora is a microcontroller board derived from the Arduino Leonardo. The Esplora differ...
Arduino Explora Pcb
The Arduino Esplora is a microcontroller board derived from the Arduino Leonardo. The Esplora differ...
-
 Diy Stepper Motor Easy Driver
A motor controller is a device or group of devices that can coordinate in a predetermined manner the...
Diy Stepper Motor Easy Driver
A motor controller is a device or group of devices that can coordinate in a predetermined manner the...
-
 Diy Arduino Pro Mini
The Arduino Pro Mini is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega168 . It has 14 digital input/out...
Diy Arduino Pro Mini
The Arduino Pro Mini is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega168 . It has 14 digital input/out...
-
MPL3115A2 Barometric Pressure, Altitude, and Temperature Sensor
48 0 0 -
-
Nintendo 64DD Replacement Shell
144 0 1 -
V2 Commodore AMIGA USB-C Power Sink Delivery High Efficiency Supply Triple Output 5V ±12V OLED display ATARI compatible shark 100W
264 4 1 -
How to measure weight with Load Cell and HX711
376 0 3 -
-
Instrumentation Input, high impedance with 16 bit 1MSPS ADC for SPI
506 0 0



















































