|
arduino IDEArduino
|
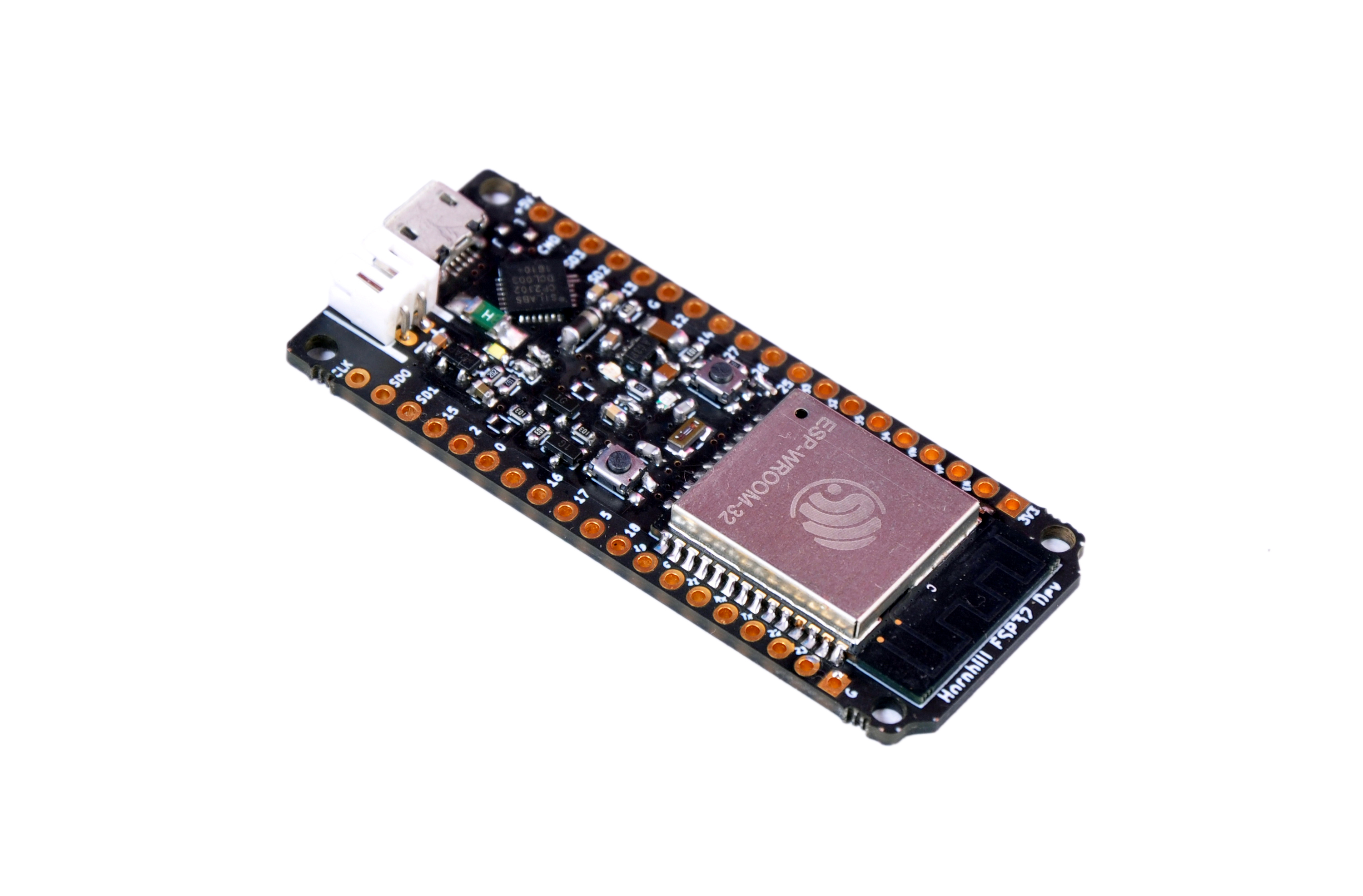
Diy ESP32 Module
ESP32 is a series of low-cost, low-power system on a chip microcontrollers with integrated Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth. The ESP32 series employs either a Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor in both dual-core and single-core variations, Xtensa LX7 dual-core microprocessor or a single-core RISC-V microprocessor and includes built-in antenna switches,
RF balun, power amplifier, low-noise receive amplifier, filters, and power-management modules. ESP32 is created and developed by Espressif Systems, a Shanghai-based Chinese company, and is manufactured by TSMC using their 40 nm process.[2] It is a successor to the ESP8266 microcontroller.
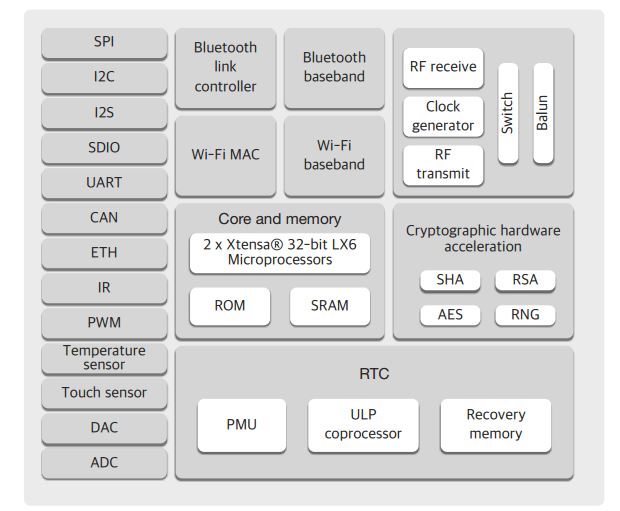
Overview of ESP32 features
You should have heard enough about the new Chip! From the specifications looks like, this is THE chip of the future, for anything connected that you want to build. Instead of using a microcontroller and add-on WiFi, Bluetooth modules for building connected things , this is the only chip you might want to use. Sounds great? But wait, this brings in a lot of programming complexity. So in this tutorial, I will run through the specifications of the chip from the perspective of practical usefulness. The things that you need to know before you start out and the features that really matter!

The block diagram below shows all that is in there! We will look at each of these blocks and see what they mean when using ESP32 in your project/product.
The Dual Core Processor
Do away with the external micro-controller/Arduino when building connected things....
The predecessor of ESP32, the ESP8266 has a builtin processor. However due to multitasking involved in updating the WiFi stack, most of the applications use a separate micro-controller for data processing, interfacing sensors and digital Input Output. With the ESP32 you may not want to use an additional micro-controller. ESP32 has Xtensa? Dual-Core 32-bit LX6 microprocessors, which runs up to 600 DMIPS. The ESP32 will run on breakout boards and modules from 160Mhz upto 240MHz . That is very good speed for anything that requires a microcontroller with connectivity options.
The two cores are named Protocol CPU (PRO_CPU) and Application CPU (APP_CPU). That basically means the PRO_CPU processor handles the WiFi, Bluetooth and other internal peripherals like SPI, I2C, ADC etc. The APP_CPU is left out for the application code. This differentiation is done in the Espressif Internet Development Framework (ESP-IDF). ESP-IDF is the official software development framework for the chip. Arduino and other implementations for the development will be based on ESP-IDF.
ESP-IDF uses freeRTOS for switching between the processors and data exchange between them. We have done numerous tutorials on freeRTOS and with all the bare-metal programming tutorials for ESP32 we will try and cover this aspect in detail. Although the feature set is great at the price at which the chip is being sold, the complexity is enormous. For the chip to get widely adopted, it will require huge efforts from Espressif as well as the community.
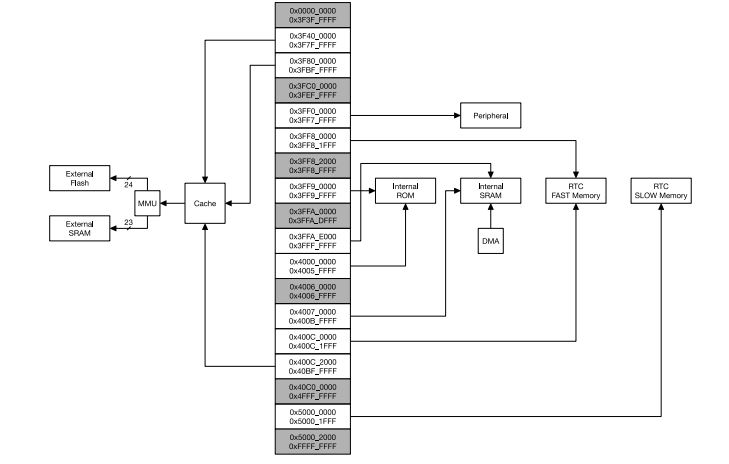
Internal Memory
The processors have closely tied internal memory for the following usage:
448 KBytes ROM for booting and core functions.
520 KBytes on-chip SRAM for data and instruction.
8 KBytes SRAM in RTC, which is called RTC SLOW Memory and can be accessed by the co-processor
during the Deep-sleep mode.
8 KBytes SRAM in RTC, which is called RTC FAST Memory and can be used for data storage; it is accessed
by the main CPU during RTC Boot from the Deep-sleep mode.
1 Kbit of EFUSE, of which 256 bits are used for the system (MAC address and chip configuration) and the remaining 768 bits are reserved for customer applications, including Flash-Encryption and Chip-ID
External Flash and SRAM
Most of the modules like ESP32 Wroom use external Flash-W25Q32 (4M Bytes!) for storing the application code. The chip supports 4 x 16 MBytes of external QSPI flash and SRAM with hardware encryption based on AES.
ESP32 accesses the external QSPI flash and SRAM through high-speed caches.
Up to 16 MBytes of external flash are memory-mapped onto the CPU code space, supporting 8, 16 and 32-bit access. Code execution is supported.
Up to 8 MBytes of external SRAM are memory-mapped onto the CPU data space, supporting 8, 16 and 32-bit access. Data-read is supported on the flash and SRAM. Data-write is supported on the SRAM.
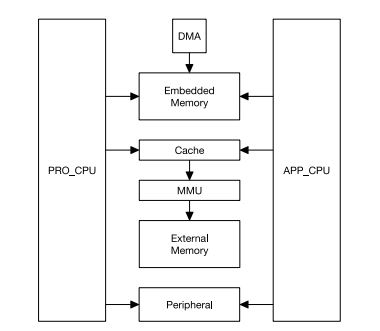
Since the processor architecture is 32 bit. The internal peripherals, the wifi, Bluetooth, External Memories etc are mapped to 2^32 (4GB) address space.
Also one interesting thing to note is that the both processors are mapped symmetrically to this address space. It basically means, a register for example can be accessed from same address location from both the CPUs as shown in image below.
So looking at these features form the project/product development perspective, you can do away with an external micro-controller/Arduino. However it brings complexity of switching between the processors and handling the application data. It will not be a one way street as with normal micro-controller development. We will be exploring this in the numerous tutorials that we plan to do.
The WiFi
ESP32 implements TCP/IP, full 802.11 b/g/n/e/i WLAN MAC protocol, and Wi-Fi Direct specification. This means ESP 32 can speak to most of the WiFi Routers out there when used in station(client) mode. Also it is able to create an Access point with full 802.11 b/g/n/e/i.
ESP32 also supports the Wi-Fi Direct . Wifi-Direct is good option for peer-to-peer connection without the need of a access point. The Wifi-Direct is easier to setup and the data transfer speeds are much better than bluetooth. This could potential be used to configure ESP32 based projects from a phone/tablet that supports WiFi direct. There is no code example in the ESP-IDF SDK at the time of the writing. The ESP-IDF WiFi implementation has following features in the development:
Infrastructure BSS Station mode / P2P mode / softAP mode support
P2P Discovery, P2P Group Owner, P2P Group Client and P2P Power Management
WPA/WPA2-Enterprise and WPS driver
All the features we have looked so far, all packed in 48 pin QFN package size 6mm x 6mm. [Image here] A better picture to look at is the pinout diagram for the ESP Wroom32 breakout.
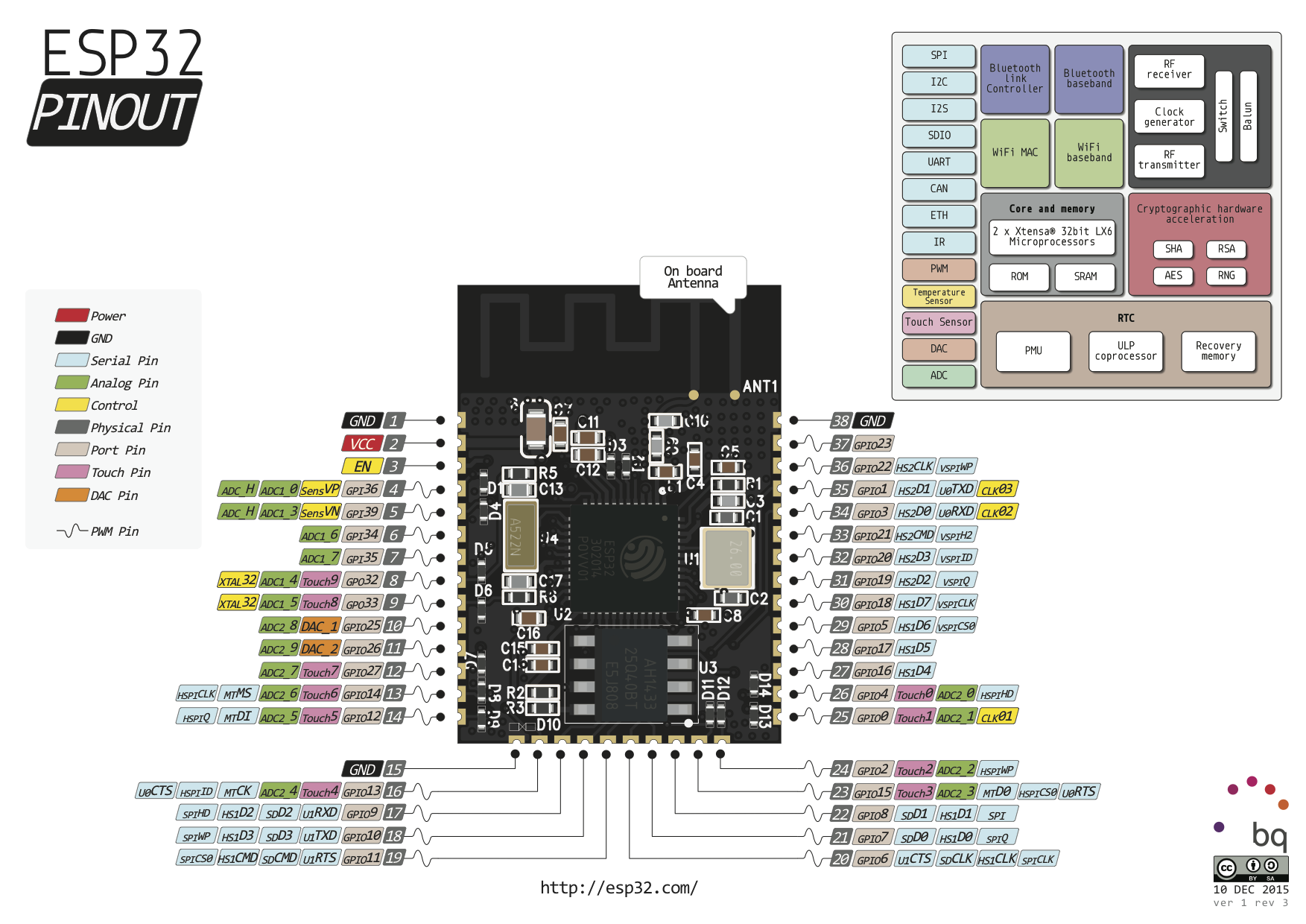
We plan to make several boards with ESP32. We are currently working on Hornbill ESP32. It is based on Wroom32 and comes with a built-in single cell LiPo charger.
ESP32 is power packed with hardware features. The high speed dual core processors along with the numerous built in peripherals it is set to replace micro-controllers in connected products. The WiFi, Bluetooth Classic and BLE make it great choice to build anything connected. Even if a project does not require a particular feature initially, it could be utilized as required. The built-in hardware accelerator enables secure code storage and securely connecting to the Internet with TLS (SSL). Apart from this the "out of the box" peripheral like the Infrared Remote Controller will be used in numerous hacks!
The software/firmware will be key to success of ESP32. It uses freeRTOS to handle multitasking. The number of peripherals, wireless connectivity, dual core processors and the overall architecture needs to be understood thoroughly to build reliable, responsive , secure and robust products and projects. We plan to do explore, it in depth. Signup to receive notifications as we go along building stuff with the chip of the future
Update
Some of you have also raised concerned about the reliability and WiFi performance of the chip for industrial grade applications. The specifications suggest that the chip should be able to perform well, however a lot depends on the hardware design of the end product. Also, while working on the previous version of the chip people had complained of the reset issues, digging deep we found out that several of these issues were improper structuring of the code. The chip uses RTOS to multitask, keep the WiFi stack refreshed. If certain rules are not followed during code it will result chip reset, wifi reset etc. In one of the tutorials we will try and cover this aspect. So remember if the chip is behaving erratic, it could be code as well.



Diy ESP32 Module
*PCBWay community is a sharing platform. We are not responsible for any design issues and parameter issues (board thickness, surface finish, etc.) you choose.
- Comments(0)
- Likes(1)
-
 Engineer
Sep 26,2022
Engineer
Sep 26,2022
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by Sreeram.zeno
More by Sreeram.zeno
-
 Esp12-F Cluster V1.0
The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip, with built-in TCP/IP networking software, and microcontro...
Esp12-F Cluster V1.0
The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip, with built-in TCP/IP networking software, and microcontro...
-
 TB6612FNG Motor Driver
The TB6612FNG Motor Driver can control up to two DC motors at a constant current of 1.2A (3.2A peak)...
TB6612FNG Motor Driver
The TB6612FNG Motor Driver can control up to two DC motors at a constant current of 1.2A (3.2A peak)...
-
 Sunny Buddy Solar Charger v1.0
This is the Sunny Buddy, a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) solar charger for single-cell LiPo ba...
Sunny Buddy Solar Charger v1.0
This is the Sunny Buddy, a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) solar charger for single-cell LiPo ba...
-
 Diy 74HC4051 8 Channel Mux Breakout Pcb
The 74HC4051; 74HCT4051 is a single-pole octal-throw analog switch (SP8T) suitable for use in analog...
Diy 74HC4051 8 Channel Mux Breakout Pcb
The 74HC4051; 74HCT4051 is a single-pole octal-throw analog switch (SP8T) suitable for use in analog...
-
 Diy RFM97CW Breakout Pcb
IntroductionLoRa? (standing for Long Range) is a LPWAN technology, characterized by a long range ass...
Diy RFM97CW Breakout Pcb
IntroductionLoRa? (standing for Long Range) is a LPWAN technology, characterized by a long range ass...
-
 ProMicro-RP2040 Pcb
The RP2040 is a 32-bit dual ARM Cortex-M0+ microcontroller integrated circuit by Raspberry Pi Founda...
ProMicro-RP2040 Pcb
The RP2040 is a 32-bit dual ARM Cortex-M0+ microcontroller integrated circuit by Raspberry Pi Founda...
-
 Serial Basic CH340G Pcb
A USB adapter is a type of protocol converter that is used for converting USB data signals to and fr...
Serial Basic CH340G Pcb
A USB adapter is a type of protocol converter that is used for converting USB data signals to and fr...
-
 Mp3 Shield For Arduino
Hardware OverviewThe centerpiece of the MP3 Player Shield is a VS1053B Audio Codec IC. The VS1053B i...
Mp3 Shield For Arduino
Hardware OverviewThe centerpiece of the MP3 Player Shield is a VS1053B Audio Codec IC. The VS1053B i...
-
 MRK CAN Shield Arduino
The CAN-BUS Shield provides your Arduino or Redboard with CAN-BUS capabilities and allows you to hac...
MRK CAN Shield Arduino
The CAN-BUS Shield provides your Arduino or Redboard with CAN-BUS capabilities and allows you to hac...
-
 AVR ISP Programmer
AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology ...
AVR ISP Programmer
AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology ...
-
 Diy Arduino mega Pcb
The Arduino Mega 2560 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560. It has 54 digital input/ou...
Diy Arduino mega Pcb
The Arduino Mega 2560 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560. It has 54 digital input/ou...
-
 Max3232 Breakout Board
MAX3232 IC is extensively used for serial communication in between Microcontroller and a computer fo...
Max3232 Breakout Board
MAX3232 IC is extensively used for serial communication in between Microcontroller and a computer fo...
-
 Line Follower Pcb
The Line Follower Array is a long board consisting of eight IR sensors that have been configured to ...
Line Follower Pcb
The Line Follower Array is a long board consisting of eight IR sensors that have been configured to ...
-
 HMC6343 Accelerometer Module
The HMC6343 is a solid-state compass module with tilt compensation from Honeywell. The HMC6343 has t...
HMC6343 Accelerometer Module
The HMC6343 is a solid-state compass module with tilt compensation from Honeywell. The HMC6343 has t...
-
 RTK2 GPS Module For Arduino
USBThe USB C connector makes it easy to connect the ZED-F9P to u-center for configuration and quick ...
RTK2 GPS Module For Arduino
USBThe USB C connector makes it easy to connect the ZED-F9P to u-center for configuration and quick ...
-
 Arduino Explora Pcb
The Arduino Esplora is a microcontroller board derived from the Arduino Leonardo. The Esplora differ...
Arduino Explora Pcb
The Arduino Esplora is a microcontroller board derived from the Arduino Leonardo. The Esplora differ...
-
 Diy Stepper Motor Easy Driver
A motor controller is a device or group of devices that can coordinate in a predetermined manner the...
Diy Stepper Motor Easy Driver
A motor controller is a device or group of devices that can coordinate in a predetermined manner the...
-
 Diy Arduino Pro Mini
The Arduino Pro Mini is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega168 . It has 14 digital input/out...
Diy Arduino Pro Mini
The Arduino Pro Mini is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega168 . It has 14 digital input/out...
-
Atomic Force Microscope - electronic part
25 0 0 -
-
-
DIY Fiber Laser Tube Cutting Machine
95 0 1 -
-
-
DIY Transistor Tester | Build Your Own LCR Meter at Home with Arduino Nano
253 0 3 -