|
Arduino Web Editor |
STM32 SPI Communcation and Data Sent
SPI in STM32F103C8
Comparing SPI bus in Arduino & STM32F103C8 Blue Pill board, STM32 has 2 SPI bus in it while Arduino Uno has one SPI bus. Arduino Uno has ATMEGA328 microcontroller in it, and STM32F103C8 has ARM Cortex- M3 which makes it faster than Arudino Board.

STM32 SPI Programming
The programming is similar to the Arduino code. The same <SPI.h> library is used in programming STM32F103C8. It can be programmed using USB port without using FTDI programmer, to learn more about programming STM32 with Arduino IDE follow the link.
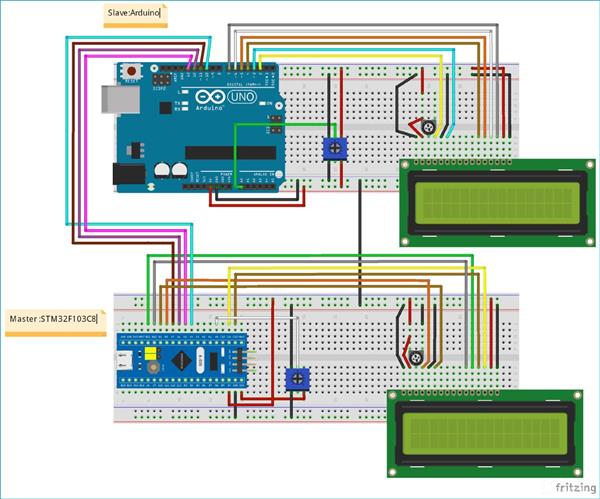
In this STM32 SPI Example, we will use Arduino UNO as Slave and STM32F103C8 as Master with Two 16X2 LCD display attached to each other separately. Two Potentiometers are also connected with STM32 (PA0) and Arduino (A0) to determine the sending values (0 to 255) from master to slave and slave to master by varying the potentiometer.
Analog input is taken at STM32F10C8 pin PA0 (0 to 3.3V) by rotating the potentiometer. Then this input value is converted into Analog to Digital value (0 to 4096) and this digital value is further mapped to (0 to 255) as we can send only 8-bit (byte) data through SPI communication at once.
Similarly in Slave side we take analog input value at Arduino pin A0 from (0 to 5V) by using potentiometer. And again this input value is converted into Analog to Digital value (0 to 1023) and this digital value is further mapped to (0 to 255)
Master STM32 SPI Programming Explanation
1. First of all we need to include the SPI library for using SPI communication functions and LCD library for using LCD functions. Also define LCD pins for 16x2 LCD. Learn more about interfacing LCD with STM32 here.
#include<SPI.h>
#include<LiquidCrystal.h>
const int rs = PB0, en = PB1, d4 = PB10 , d5 = PB11 , d6 = PC13, d7 = PC14;
LiquidCrystal lcd(rs,en,d4,d5,d6,d7);
2. In void setup()
Start Serial Communication at Baud Rate 9600.
Serial.begin(9600);
Next begin the SPI communication
SPI.begin();
Then set the Clock divider for SPI communication. I have set divider 16.
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV16);
Next set the SS pin HIGH since we didn’t start any transfer to slave arduino.
digitalWrite(SS,HIGH);
3. In void loop()
Before sending any value to slave we need to LOW the slave select value to begin transfer to slave from master.
digitalWrite(SS, LOW);
Next read the analog value from the master STM32F10C8 POT attached to pin PA0.
int pot = analogRead(PA0);
Then convert this value in terms of one byte (0 to 255).
byte MasterSend = map(pot,0,4096,0,255);
Here comes the important step, in the following statement we send the converted POT value stored in Mastersend variable to the slave Arduino, and also receive value from slave Arduino and stored that in mastereceive variable.
Mastereceive = SPI.transfer(Mastersend);
Next display those received values from the slave arduino with a delay of 500 microseconds and then continuously receive and display the values.
Serial.println("Slave Arduino to Master STM32");
Serial.println(MasterReceive lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Master: STM32");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("SalveVal:");
lcd.print(MasterReceive delay(500);
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH);

Master STM32 SPI
//SPI Master code for STM32F103C8
//SPI Communication between STM32 & Arduino
//Circuit Digest
#include<SPI.h> // Including Library for using SPI Communication
#define SS PA4
#include<LiquidCrystal.h> // Including LCD display library
const int rs = PB0, en = PB1, d4 = PB10 , d5 = PB11 , d6 = PC13, d7 = PC14; // Declaring pin names and pin numbers of lcd
LiquidCrystal lcd(rs,en,d4,d5,d6,d7); // Setting lcd and its paramaters
void setup (void)
{
lcd.begin(16,2); // Setting lcd as 16x2 mode
lcd.setCursor(0,0); // Setting cursor at first row and first column
lcd.print("CIRCUIT DIGEST"); // Puts CIRCUIT DIGEST in LCD
delay(3000); // Delays for 3 seconds
lcd.clear(); // Clears lcd display
Serial.begin(9600); // Starts Serial Communication at Baud Rate 9600
pinMode(SS,OUTPUT); // Puts SS as Output
SPI.begin(); // Begins the SPI commnuication
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV16); // Sets clock for SPI communication at 16 (72/16=4.5Mhz)
digitalWrite(SS,HIGH); // Setting SlaveSelect as HIGH (So master doesnt connnect with slave)
}
void loop(void)
{
byte MasterSend,MasterReceive;
int pot = analogRead(PA0); // Analog read the input pot value at pin PA0
MasterSend = map(pot,0,4096,0,255); // Used to convert pot value in terms of 0 to 255 from 0 to 4096
digitalWrite(SS, LOW); // Starts communication with Slave connected to master
MasterReceive=SPI.transfer(MasterSend); // Send the mastersend value to slave also receives value from slave
Serial.println("Slave Arduino to Master STM32"); // Used in Serial Monitor
Serial.println(MasterReceive); // Puts value Received im Serail Monitor
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Master: STM32");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("SalveVal:");
lcd.print(MasterReceive); // Puts the received value from slave arduino
delay(500);
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH); // Again make SS line HIGH so that it doesnt communicate with Slave
lcd.clear();
}
Slave Arduino SPI
//SPI Slave Code for Arduino
//SPI Communication between STM32F103C8 & Arduino
//Circuit Digest
#include<SPI.h> // Including Library for using SPI Communication
#include<LiquidCrystal.h> // Including LCD display library
LiquidCrystal lcd(2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7); // Define LCD Module Pins (RS,EN,D4,D5,D6,D7)
volatile boolean received;
volatile byte SlaveReceived,Slavesend;
void setup()
{
lcd.begin(16,2); // Initilize LCD display
lcd.setCursor(0,0); // Sets Cursor at first line of Display
lcd.print("CIRCUIT DIGEST"); // Prints CIRCUIT DIGEST in LCD
delay(3000); // Delay for 3 seconds
lcd.clear(); // Clears LCD display
Serial.begin(9600); // Starts Serial Communication at Baud Rate 9600
pinMode(MISO,OUTPUT); // Sets MISO as OUTPUT (Have to Send data to Master IN (STM32F103C8)
SPCR |= _BV(SPE); // Turn on SPI in Slave Mode
received = false;
SPI.attachInterrupt(); // Interuupt ON is set for SPI commnucation
}
ISR (SPI_STC_vect) // Inerrrput routine function
{
SlaveReceived = SPDR; // Value received from master STM32F103C8 is stored in variable slavereceived
received = true; // Sets received as True
}
void loop()
{
int pot = analogRead(A0); // Analog read the input pot value from analog pin A0
Slavesend = map(pot,0,1023,0,255); // Converts the value pot (0-1023) to (0-255) for sending to master stm32
SPDR = Slavesend; // Sends the salvesend value to master STM32F103C8 via SPDR
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Slave: Arduino");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("MasterVal:");
Serial.println("Master STM32 to Slave Arduino");
Serial.println(SlaveReceived); // Puts the received value from Master STM32F103C8 at Serial Monitor
lcd.print(SlaveReceived); // Puts the received value from Master STM32F103C8 at LCD display
delay(500);
lcd.clear();
}
By rotating the Potentiometer at one side, you can see the varying values on LCD on another side:

So this is how SPI communication takes place in STM32. Now you can interface any SPI sensor with STM32 board.
The complete coding for Master STM32 and Slave Arduino is given above

Master STM32 SPI
//SPI Master code for STM32F103C8
//SPI Communication between STM32 & Arduino
//Circuit Digest
#include<SPI.h> // Including Library for using SPI Communication
#define SS PA4
#include<LiquidCrystal.h> // Including LCD display library
const int rs = PB0, en = PB1, d4 = PB10 , d5 = PB11 , d6 = PC13, d7 = PC14; // Declaring pin names and pin numbers of lcd
LiquidCrystal lcd(rs,en,d4,d5,d6,d7); // Setting lcd and its paramaters
void setup (void)
{
lcd.begin(16,2); // Setting lcd as 16x2 mode
lcd.setCursor(0,0); // Setting cursor at first row and first column
lcd.print("CIRCUIT DIGEST"); // Puts CIRCUIT DIGEST in LCD
delay(3000); // Delays for 3 seconds
lcd.clear(); // Clears lcd display
Serial.begin(9600); // Starts Serial Communication at Baud Rate 9600
pinMode(SS,OUTPUT); // Puts SS as Output
SPI.begin(); // Begins the SPI commnuication
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV16); // Sets clock for SPI communication at 16 (72/16=4.5Mhz)
digitalWrite(SS,HIGH); // Setting SlaveSelect as HIGH (So master doesnt connnect with slave)
}
void loop(void)
{
byte MasterSend,MasterReceive;
int pot = analogRead(PA0); // Analog read the input pot value at pin PA0
MasterSend = map(pot,0,4096,0,255); // Used to convert pot value in terms of 0 to 255 from 0 to 4096
digitalWrite(SS, LOW); // Starts communication with Slave connected to master
MasterReceive=SPI.transfer(MasterSend); // Send the mastersend value to slave also receives value from slave
Serial.println("Slave Arduino to Master STM32"); // Used in Serial Monitor
Serial.println(MasterReceive); // Puts value Received im Serail Monitor
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Master: STM32");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("SalveVal:");
lcd.print(MasterReceive); // Puts the received value from slave arduino
delay(500);
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH); // Again make SS line HIGH so that it doesnt communicate with Slave
lcd.clear();
}
Slave Arduino SPI
//SPI Slave Code for Arduino
//SPI Communication between STM32F103C8 & Arduino
//Circuit Digest
#include<SPI.h> // Including Library for using SPI Communication
#include<LiquidCrystal.h> // Including LCD display library
LiquidCrystal lcd(2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7); // Define LCD Module Pins (RS,EN,D4,D5,D6,D7)
volatile boolean received;
volatile byte SlaveReceived,Slavesend;
void setup()
{
lcd.begin(16,2); // Initilize LCD display
lcd.setCursor(0,0); // Sets Cursor at first line of Display
lcd.print("CIRCUIT DIGEST"); // Prints CIRCUIT DIGEST in LCD
delay(3000); // Delay for 3 seconds
lcd.clear(); // Clears LCD display
Serial.begin(9600); // Starts Serial Communication at Baud Rate 9600
pinMode(MISO,OUTPUT); // Sets MISO as OUTPUT (Have to Send data to Master IN (STM32F103C8)
SPCR |= _BV(SPE); // Turn on SPI in Slave Mode
received = false;
SPI.attachInterrupt(); // Interuupt ON is set for SPI commnucation
}
ISR (SPI_STC_vect) // Inerrrput routine function
{
SlaveReceived = SPDR; // Value received from master STM32F103C8 is stored in variable slavereceived
received = true; // Sets received as True
}
void loop()
{
int pot = analogRead(A0); // Analog read the input pot value from analog pin A0
Slavesend = map(pot,0,1023,0,255); // Converts the value pot (0-1023) to (0-255) for sending to master stm32
SPDR = Slavesend; // Sends the salvesend value to master STM32F103C8 via SPDR
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Slave: Arduino");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("MasterVal:");
Serial.println("Master STM32 to Slave Arduino");
Serial.println(SlaveReceived); // Puts the received value from Master STM32F103C8 at Serial Monitor
lcd.print(SlaveReceived); // Puts the received value from Master STM32F103C8 at LCD display
delay(500);
lcd.clear();
}
STM32 SPI Communcation and Data Sent
- Comments(0)
- Likes(0)
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by electronicguru0007
More by electronicguru0007
-
 How to make an alarm clock with pic microcontroller
he five push buttons will act as an input for setting the alarm for the required time. So one end of...
How to make an alarm clock with pic microcontroller
he five push buttons will act as an input for setting the alarm for the required time. So one end of...
-
 How to make RMS to DC Converter using IC AD736
A True-RMS or TRMS is a type of converter which converts RMS value to equivalent DC value. Here in t...
How to make RMS to DC Converter using IC AD736
A True-RMS or TRMS is a type of converter which converts RMS value to equivalent DC value. Here in t...
-
 STM32 SPI Communcation and Data Sent
SPI in STM32F103C8Comparing SPI bus in Arduino & STM32F103C8 Blue Pill board, STM32 has 2 SPI bu...
STM32 SPI Communcation and Data Sent
SPI in STM32F103C8Comparing SPI bus in Arduino & STM32F103C8 Blue Pill board, STM32 has 2 SPI bu...
-
 How to Communicate Arduinos via RS-485
What project will you develop?The project consists of 3 Arduino's. We have an Arduino UNO, a Nano, a...
How to Communicate Arduinos via RS-485
What project will you develop?The project consists of 3 Arduino's. We have an Arduino UNO, a Nano, a...
-
 PIC16F877A Temperature and Humidity Measurement Board
Temperature and Humidity measurement is often useful in many applications like Home Automation, Envi...
PIC16F877A Temperature and Humidity Measurement Board
Temperature and Humidity measurement is often useful in many applications like Home Automation, Envi...
-
 Diy Buck Converter
n the field of DC-DC Converters, A single-ended primary-inductor converter or SEPIC converter is a t...
Diy Buck Converter
n the field of DC-DC Converters, A single-ended primary-inductor converter or SEPIC converter is a t...
-
 Iot AC Current Measuring System
Smart power monitoring is getting increasingly popular to improve energy efficiency in medium/small ...
Iot AC Current Measuring System
Smart power monitoring is getting increasingly popular to improve energy efficiency in medium/small ...
-
 ESP32 Weather Station
In this project, we will learn how to create a weather station, which will display reading from a BM...
ESP32 Weather Station
In this project, we will learn how to create a weather station, which will display reading from a BM...
-
 NRF Data Transfer Via 2 Boards
There are various wireless communication technologies used in building IoT applications and RF (Radi...
NRF Data Transfer Via 2 Boards
There are various wireless communication technologies used in building IoT applications and RF (Radi...
-
 Iot patient monitoring system
When we are talking about major vital signs of a human body, there are four major parameters that we...
Iot patient monitoring system
When we are talking about major vital signs of a human body, there are four major parameters that we...
-
 Setting up zigbee communication with nodemcu and arduino
Zigbee is a popular wireless communication protocol used to transfer a small amount of data with ver...
Setting up zigbee communication with nodemcu and arduino
Zigbee is a popular wireless communication protocol used to transfer a small amount of data with ver...
-
 Ac Dimmer Remote PCB
The brightness can be controlled using the IR remote of TV, DVD, etc. Dimming Control system using M...
Ac Dimmer Remote PCB
The brightness can be controlled using the IR remote of TV, DVD, etc. Dimming Control system using M...
-
 Esp32 Home Automation
There are relay modules whose electromagnet can be powered by 5V and with 3.3V. Both can be used wit...
Esp32 Home Automation
There are relay modules whose electromagnet can be powered by 5V and with 3.3V. Both can be used wit...
-
 Lora Communication With Network
This was a very simple project and can come in handy for various applications. But what it can't do ...
Lora Communication With Network
This was a very simple project and can come in handy for various applications. But what it can't do ...
-
 GPS Module Based Tracking Device Pcb
ESP32 GPS vehicle tracker using NEO 6M GPS module and Arduino IDE. With the help of this GPS tracker...
GPS Module Based Tracking Device Pcb
ESP32 GPS vehicle tracker using NEO 6M GPS module and Arduino IDE. With the help of this GPS tracker...
-
 Traffic Management for Emergency Vehicles using AT89S52 Microcontroller
These days’ traffic congestion is the biggest problem of densely populated cities. The project focus...
Traffic Management for Emergency Vehicles using AT89S52 Microcontroller
These days’ traffic congestion is the biggest problem of densely populated cities. The project focus...
-
 Diy Multimeter Pcb
This is a project based on Arduino board which can measureresistance, diode, continuity[H1] , voltag...
Diy Multimeter Pcb
This is a project based on Arduino board which can measureresistance, diode, continuity[H1] , voltag...
-
 Live Instagram Followers Pcb
ESP8266 is capable of functioning reliably in industrial environments, with an operating temperature...
Live Instagram Followers Pcb
ESP8266 is capable of functioning reliably in industrial environments, with an operating temperature...
-
-
AEL-2011 Power Supply Module
515 0 2 -
AEL-2011 50W Power Amplifier
474 0 2 -
-
-
Custom Mechanical Keyboard
691 0 0 -
Tester for Touch Screen Digitizer without using microcontroller
322 2 2 -
Audio reactive glow LED wristband/bracelet with NFC / RFID-Tags
306 0 1 -
-
-